What are BIM Dimensions?
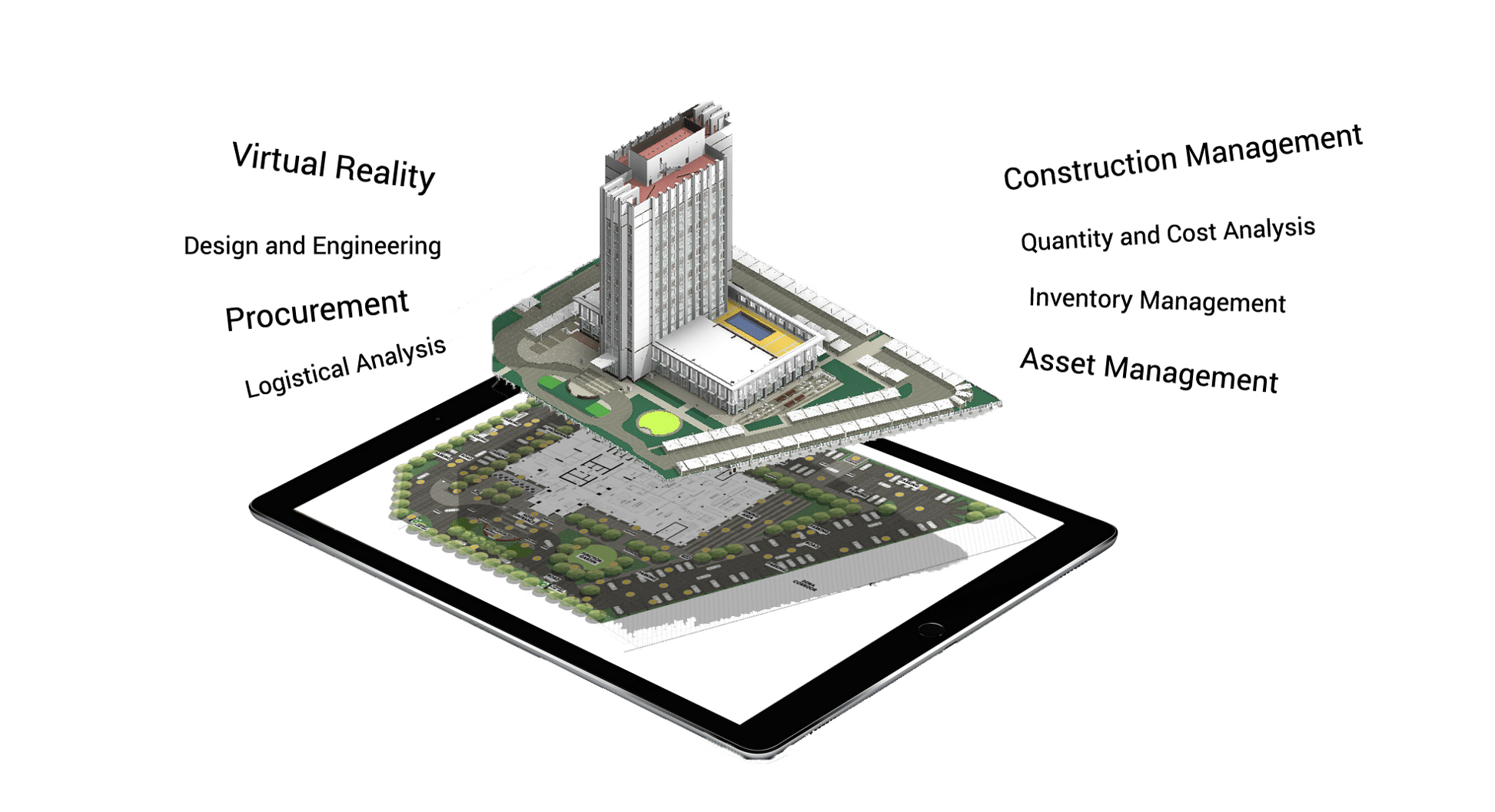
BIM dimensions, also known as Building Information Modeling dimensions, refer to different aspects or levels of information within a BIM model. These dimensions are used to describe and categorize the various levels of detail and data available in a BIM model. The commonly recognized BIM dimensions are as follows:
3D (Spatial Dimension): This dimension represents the physical geometry and spatial relationships of building elements in three-dimensional space. It includes the visual representation of the building model, allowing users to view and navigate through the virtual building.
4D (Time Dimension): The 4D dimension adds the element of time to the BIM model. It involves associating scheduling and sequencing data with the building elements, enabling the visualization and simulation of construction phasing, project scheduling, and progress monitoring over time.
5D (Cost Dimension): The 5D dimension incorporates cost-related information into the BIM model. It involves associating cost data and estimating quantities with the building components. This enables the generation of accurate cost estimates, cost tracking, and analysis of cost impacts based on changes in the model.
6D (Facility Management Dimension): The 6D dimension focuses on facility management and life-cycle information. It includes integrating data such as equipment specifications, maintenance schedules, warranty information, and other relevant facility management details into the BIM model. This allows owners and facility managers to effectively manage and maintain the building after construction.
7D (Sustainability Dimension): The 7D dimension relates to sustainability analysis and environmental performance. It involves incorporating data regarding energy consumption, carbon emissions, water usage, and other environmental factors into the BIM model. This enables the evaluation of sustainable design strategies and performance analysis of the building.
It’s important to note that while the terms “4D,” “5D,” “6D,” and “7D” are commonly used to represent the different dimensions, the specific capabilities and data included may vary depending on the context, software tools, and industry practices. The primary focus of BIM is to improve collaboration, information exchange, and decision-making throughout the entire life cycle of a building project.
What is 3D BIM?
3D BIM (Building Information Modelling) refers to the use of three-dimensional digital representations of buildings or infrastructure projects, combined with data about their physical and functional characteristics. BIM is an advanced approach to construction project management that integrates various aspects of the project, including design, documentation, coordination, and collaboration.
In 3D BIM, the building or infrastructure model is created using specialized software that allows architects, engineers, and other stakeholders to generate a virtual representation of the project. This model incorporates geometric information, such as the shape, size, and spatial relationships of the building elements, as well as non-geometric data, including material specifications, performance data, cost estimates, and scheduling information.
The 3D BIM model serves as a central repository of information that can be accessed and updated by different project participants throughout the project lifecycle. It enables various professionals to collaborate more effectively, identify and resolve clashes or conflicts in design, simulate and analyze building performance, generate construction documents, and facilitate the coordination and sequencing of construction activities.
By utilizing 3D BIM, project teams can improve communication, reduce errors and rework, enhance project visualization, optimize resource allocation, and streamline construction processes. It provides a more comprehensive and accurate representation of the project, promoting better decision-making and improving overall project outcomes.
What is 4D BIM?
4D BIM (Four-Dimensional Building Information Modeling) is an extension of 3D BIM that incorporates the element of time or scheduling information into the building information model. It adds a time dimension to the three-dimensional representation of the project, allowing project teams to visualize and manage the construction process over time.
In 4D BIM, the construction schedule is linked to the 3D BIM model, associating specific tasks or activities with the corresponding elements in the model. This integration enables project teams to create a dynamic simulation of the construction process, visualizing the sequence of activities, their durations, and their dependencies on each other.
By incorporating the time dimension, 4D BIM provides several benefits:
Visualization: It allows stakeholders to visualize the construction process from start to finish, identifying potential clashes, conflicts, or bottlenecks in the schedule. This visualization aids in better understanding the construction sequence and enhances communication and coordination among team members.
Clash Detection: 4D BIM helps in detecting clashes or conflicts between different construction activities and ensures that tasks are scheduled in a way that avoids clashes and optimizes resource utilization. This clash detection feature can help identify and resolve potential issues before they occur on-site, reducing rework and delays.
Schedule Optimization: By simulating the construction process, project teams can evaluate different scheduling scenarios and identify opportunities to optimize the sequence of activities, minimize project duration, and improve overall efficiency.
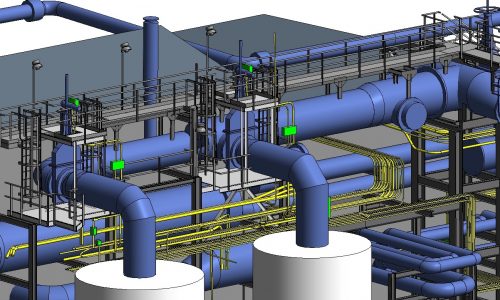
BIM 3D modeling (Building Information Modeling) is becoming increasingly significant for modern construction projects. In addition to give digital representation of a building project.
The BIM model acts as an unparalleled tool for coordination and clash detection between components of different disciplines. Trisita has experience on clash detection at all LOD on building .
4D BIM services, which is a part of building information modeling, is one step destination for all kinds of building construction in various areas like commercial, residential and industrial etc.
Even if there are no drawings or plans available, laser scanning devices can capture the real world in 3D. This information can further be utilized to develop as-built BIM Models which can be further linked to CMMS and FM systems.
We use BIM 360™ construction management software and combine mobile technologies with cloud collaboration for on-site construction management.
A detailed measurement of materials and labour required to complete a construction project is known as quantity take-offs. We at Trisita possess well experienced estimators who can do quantity take offs by reviewing drawings and specifications.
The shop drawings are generated using 3D BIM Models and hence are consistent with no scope of manual errors. If there are any updates to the model, the plans, sections, details and schedules all update in real time, ensuring correct data in every construction document.
Trisita’s 3D modeling allows architectural firms to review design elements with respect to other building systems and services on any project. Our BIM and 3D visualization allow stakeholders involved in the construction process to share project image effectively and identify errors and inconsistencies in the early stages of construction.
Trisita integrates BIM model with the facility management system and automates the preventive maintenance program. BIM helps us to connect an existing software package for supplementing data and ensuring robust maintenance.
Level of Details