
What is AWS EBS?
Amazon offers a storage service called Amazon Elastic Block Storage, or Amazon EBS, to be used with your EC2 instances in order to properly address the issues associated with data storage in the cloud. This service offers block level storage volumes with high availability. You will get in-depth information on AWS Amazon EBS Volume in this tutorial on what AWS EBS in Amazon is.
We will learn everything about EBS in this blog post on AWS EBS, which will also cover the following topics in the same order:
- What is AWS EBS in Amazon
- Types of Amazon Elastic Block Store
- Features of AWS EBS
- Benefits of AWS EBS
- Properties of Amazon Elastic Block Store
What is AWS EBS in Amazon?
Let me provide a simple explanation of AWS EBS using an example. Let’s say your computer has 120GB of storage. You purchase an external drive and connect it to your machine since you are running out of space and need more. You’re once more joyful, and life is good. With the exception of the fact that it is intended for use with your EC2 instances (virtual systems) on the AWS cloud, the Amazon EBS is analogous to that external disc.
Let’s now examine AWS EBS Volume in more technical terms.
Although Amazon does provide local storage for each EC2 Instance that you can utilize while the instance is running, the data in that local storage is also destroyed as soon as the instance is shut down. As a result, you would need Amazon EBS with your EC2 instance if you needed to save the data.
Let’s concentrate on a more technical definition of Amazon EBS now that we have a clear understanding of what EBS is in layman’s terms.
The main definition of AWS EBS is that it is a raw block-level storage solution intended for use with Amazon EC2 instances. Every block functions as a hard drive, allowing any kind of file to be stored there or even the installation of an entire operating system. To avoid data loss and component failure, each EBS volume that you attach to your EC2 instance is automatically replicated within its availability zone. With EBS, one can quickly and easily scale their consumption up or down.
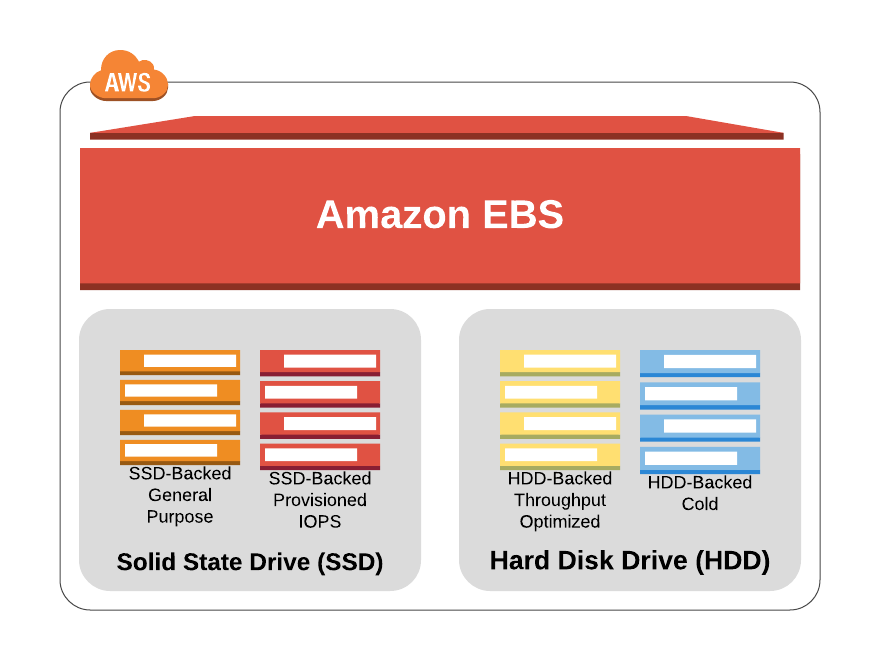
Types of Amazon Elastic Block Store:
For various workloads and use scenarios, AWS offers various EBS volume options. These various EBS volumes are all either SSD (Solid-state drive) or hard disc drive-backed (HDD).
- SSD (Solid-state drive): SSD-backed EBS Volumes are specially tuned for transactional workloads, in which the volume is expected to carry out a large number of tiny read and write operations.
- HDD (Hard Disk Drive): HDD-backed volumes were created with heavy workloads in mind.
The list below includes various EBS Volume types that fit under the SSD-backed and HDD-backed EBS Volume categories.
- Since General Purpose SSD is appropriate for small and medium workloads such regularly accessed workloads, applications in development and production settings, system boot volumes, and more, it is advised for the majority of use cases. 3 IOPS (input/output operations per second) are supported by SSD for each GB. This volume’s size ranges from 1 GiB to 16 TiB.
- Critical production applications and databases that demand high speed EBS storage typically use Provisioned IOPS SSD. The most rigorous I/O workloads can be accommodated by this kind of EBS volume. This volume’s volume size ranges from 4 GiB to 16 TiB.
- Throughput Optimized HDD applications that need a lot of storage and throughput but where IOPS are not important are the ones for which EBS Volumes are intended. such as massive data warehousing, log processing, and other techniques. This volume has a 500 GiB – 16 TiB size.
- Cold HDD is intended for workloads with fewer accesses. This volume is a magnetic storage format that works well in situations where storing data cheaply is typically the major requirement. This volume has a size of 500 GiB – 16 TiB.
Features of AWS EBS :
- Availability and durability: For all of their services, Amazon has made care to guarantee high availability and durability, and EBS is no different in this regard. Amazon replicates the EBS Volume data across many servers in an availability zone at no additional cost in order to prevent data loss. EBS volumes have an annual failure rate (AFR) of 0.1% to 0.2%, which makes them around 20 times more reliable than common commodity disc drives. Traditional disc drives have an annual failure rate of about 4%.

- Amazon EBS Snapshots: According to Amazon Web Services, an EBS Snapshot is an incremental, point-in-time duplicate of an Amazon EBS volume. All the information required to restore your data from EBS volumes is contained in snapshots. When a snapshot is made on an EBS volume for the first time, all of the block data is captured; however, in the subsequent snapshot, just the block modifications since the previous snapshot are captured (provided that the first snapshot still exists while taking the second snapshot). A block’s pictures are all connected together. When data is recovered using an EBS snapshot, both the data unique to that snapshot and the data from earlier snapshots are restored.
- EBS Encryption: For EBS Volumes, AWS also provides seamless data encryption. All data, including data on the volume, disc I/O, and even snapshots made from that encrypted volume, is encrypted when an encrypted EBS volume is mounted to an instance. A secure key management infrastructure does not need to be organized or maintained thanks to this functionality. On the servers that host EC2 instances, EBS encryption takes place. Using Amazon managed keys or keys that customers create themselves using the AWS key management Service, EBS encryption provides data protection (KMS).
Let’s examine the advantages of AWS Elastic Block Store as we continue this tutorial on what is AWS EBS.
Benefits of AWS EBS:
Reliability: EBS Volume may automatically react to its own availability Zone to avoid component failures.
Secure: Who can access which EBS Volumes can be determined using one of the several access control policies that Amazon offers.
Flexibility: EBS Volumes support live configuration changes and can be scaled up and down as needed. without disrupting service, changes to volume type, volume size, and IOPS capacity.
Easy Data Backup: Doing point-in-time snapshots of Amazon EBS volumes that are redundantly stored across different availability zones makes taking data backup simple. Whether or not the EBS Volume is connected to an instance has no bearing on whether or not a snapshot may be taken.
Properties of Amazon Elastic Block Store:
- Only one EC2 instance can have an EBS Volume assigned to it at once.
- The root volume cannot be encrypted without utilizing any of their third-party tools, although volumes other than the root volumes can be encrypted.
- When an EC2 instance is terminated, the root volumes are automatically destroyed.
- An EBS volume can be up to 16 TiB in size.
- To generate volumes in several AWS regions, a copy of the screenshots can be created between the locations.


9 Amazon Web Services (AWS) Innovations to Watch in 2023
9 Amazon Web Services innovations to watch in 2023
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is at the forefront of the ongoing innovation of the cloud. According to a Statista analysis, AWS controls over 33% of the market for cloud application development services vendors, including Machine Learning and DevSecOps. It is becoming more and more popular. And organizations are eager to use it as their preferred cloud platform. Businesses are utilizing AWS’s extensive offering of safe and dependable services. Which results in helping to cut expenses associated with IT, foster collaboration, and increase business agility.
AWS has a large range of advantages. But new developments and features are constantly being made that can further enhance the user experience. We will cover nine developments in AWS in 2023 in this blog post:

1. Cloud Security
Security is a factor that is becoming more and more crucial as businesses progressively switch to the cloud. AWS offers more compliance certifications and security standards than any other cloud platform available. And the thanks goes to Amazon’s ongoing efforts to increase the security of its platform.
The Amazon Security Lake, was unveiled on November 29, 2022. is one development in cloud security to watch for in AWS in 2023. A purpose-built security data lake that is kept in a user’s account can be created using the solution to automatically combine security data from specific sources, both on-premises and in the cloud. Users may easily evaluate security data once it is enabled, giving them a positive image of their security throughout the entire enterprise.
We may anticipate even more advancements from AWS in the field of cloud security in the future.
2. Web3 – Blockchain
The cloud application development services sector is experiencing exponential economic experimentation, and blockchain is one of the trendiest subjects in technology right now. Crypto networks are a cutting-edge method of balancing national and international investments, and AWS is already in the lead with its managed Blockchain solution.
Web3 Labs, a complete Web3 section under the umbrella of Amazon, “provides the insights platform and developer tools to support your Blockchain journey,” in the company’s own words. Beginning in 2023, Web3 will gain popularity, which will accelerate the transition away from the centralised dominating powerhouses of the webspace.
3. Performance
Performance efficiency is more crucial than ever as businesses depend on the cloud more and more for mission-critical applications. Performance efficiency is basically the capacity of an organization’s task to swiftly and effectively adapt to changes in users’ expectations.
A number of agent performance evaluation tools were made available by Amazon Connect on November 29, 2022, enabling contact centre administrators to create assessment forms with criteria.
AWS is continually working to enhance the performance of its services, so in the future, we may anticipate even greater advancements in this area.

4. DevSecOps Improvements
Security testing is included into the software development process at each level using a process called DevSecOps. A critical component of the app delivery pipeline, security is made a priority with appropriate DevSecOps integration, allowing app developers to receive timely and pertinent feedback while designing and developing their apps. AWS has introduced various capabilities, such as AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) Roles for Amazon EC2, AWS CloudFormation StackSets, and AWS Config Rules, to assist users in implementing DevSecOps. The new DevSecOps category for the AWS DevOps Competency has made it simple to locate verified AWS Partners providing DevSecOps solutions.
5. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are two other fields in which AWS has made significant investments in recent years (ML). Companies are utilising these technologies in a wide range of ways, from enhancing the precision of search results to offering more individualised recommendations.
Amazon Personalize, a service that enables developers to quickly make tailored recommendations for their consumers, is one of the most important recent contributions in this area. It generates recommendations for a user based on learning about their likes and behaviour using ML algorithms.
In its Amazon Lex service, which enables programmers to create conversational bots, AWS also uses AI and ML. Natural language processing (NLP) is used by Amazon Lex to comprehend client inquiries and then provide appropriate answers.
These technologies are also being used by AWS to increase the precision of its search results. Additionally, the OpenSearch Service now employs ML to deliver more accurate and pertinent search results.
Amazon Web Services, Inc. (AWS), a provider of end-to-end machine learning (ML) services, unveiled eight new features for Amazon SageMaker on November 30, 2022, at the AWS re:Invent executive meeting in Las Vegas. The following are some of the new capabilities:
- Role Manager: simplifies the procedures for creating permissions and restricting access for better ML governance by administrators.
- SageMaker Model Cards: simplifies the model data documentation and review procedures across the entire ML lifetime.
- Model Dashboard: provides a single interface for tracking models, reviewing historical trends, and evaluating performance.
- Amazon SageMaker Studio Notebooks: This new data preparation feature gives users the opportunity to quickly and visually inspect and resolve data-quality problems. Additionally, it enables real-time collaboration among data science teams.
- Support for geospatial data: Customers may more quickly create ML models for climate science, urban planning, and catastrophe response.
- Customers may now immediately transform the notebook into jobs that are ready for production.
- Customers can now test new models using real-time inference queries thanks to automated model validation. The new Amazon SageMaker features, according to Bratin Saha, vice president of AI and ML at AWS, will make it even simpler for teams to expedite the end-to-end development and deployment of ML models.
6. Aurora Zero-ETL Integration with Amazon Redshift
This is yet another significant development that was unveiled at the AWS reimagine CEO event in 2022. It allows for almost immediate analytics. Now, it just takes a few seconds after putting transactional data into Aurora for Amazon Redshift to get the data. Users can now use analytics and other features of Amazon Redshift to get knowledge from transactional and other data.
7. Amazon OpenSearch Serverless- You can execute your apps using the serverless computing concept of cloud computing without setting up or managing any servers. Users are able to manage all the services they would require to create and run an application on the AWS system through the architecture of AWS Serverless Computing. The latest release of Amazon OpenSearch Serverless by Amazon Web Services, Inc. (AWS) makes it simpler to execute petabyte-scale search and analytics workloads without the need to configure, manage, or scale OpenSearch clusters. Users will only be required to pay for the resources they utilise thanks to this development. Amazon MSK Serverless, Amazon EMR Serverless, and Amazon Redshift Serverless are more serverless services that the company has recently launched.

8. AWS Data Zone
AWS Data Zone was unveiled by Amazon Web Services Inc. (AWS) at the 2022 AWS re:Invent executives meeting. This data management solution streamlines and expedites a number of customer operations, including categorising, sharing, and managing on-premises data across AWS and outside sources.
The new data management solution not only streamlines procedures for users, but also makes it simple for data stewards and administrators to control and regulate access to data. In order to use and cooperate with data to gain insights, it also makes it simple for analysts, product managers, engineers, and data scientists to access data throughout the entire organization.
9. AWS Supply Chain
At the 2022 AWS reinvent conference, Amazon Web Services Inc. (AWS) unveiled another innovation. AWS Supply Chain is a brand-new cloud service that improves supply chain visibility and offers users useful insights to lower costs and minimize risks. Users may integrate their supply chain data from EDI, SAP, and other sources with only a few clicks.
According to Diego Pantoja-Navajas, vice president of AWS Supply Chain, the business will keep investing in AWS Supply Chain to help clients resolve their most challenging supply chain problems.

The Top 5 Cloud Computing Craze In This Year
In recent years, cloud computing has seen a remarkable transformation, revolutionizing the way businesses work and create. As we go into the new year, it’s critical to stay current on the newest trends affecting this market. In this blog, we’ll look at the top five trends that will dominate 2023 and change the way businesses use the cloud.
We can anticipate that businesses will continue to use cloud services in 2023 to access cutting-edge technology and improve internal operations and processes.
We mentioned in our previous blog, What Separates Mobile And Cloud Computing From One Another?, that we will learn about some of the top trends. So, here is a list of some of the trends that we think will be most significant.
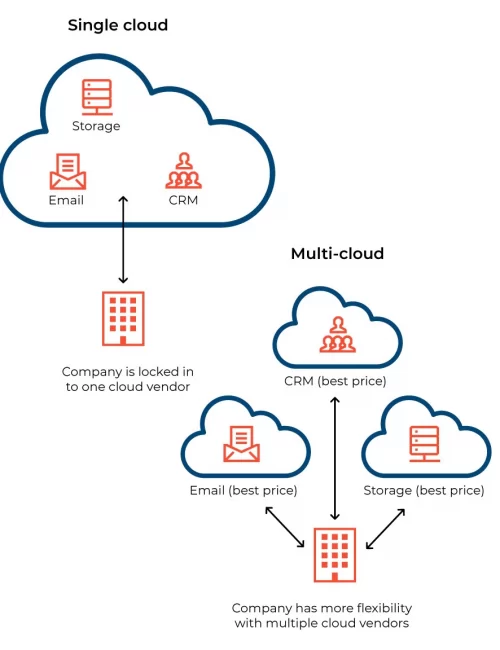
1. Multi-Cloud Computing Strategy:
The usage of multi-cloud methods is gaining traction in 2023. Organisations are realising the value of diversifying their cloud service providers in order to reduce risks, improve performance and save costs. Multi-cloud setups allow businesses to choose the finest services from various providers, avoiding vendor lock-in and boosting flexibility. This trend is pushing innovation in workload management and orchestration across various cloud computing platforms.
2. Edge Computing Integration:
Another popular trend this year is edge computing. Edge computing is developing a way to minimize latency and enhance data processing efficiency with the increasing expansion of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and applications demanding real-time processing. Cloud providers are increasingly delivering services that seamlessly integrate edge computing capabilities, allowing businesses to handle data closer to the source and improve overall system efficiency and responsiveness.

3. Serverless Computing Advancements:
Serverless computing is progressing past its early phases, with increased capabilities and acceptance rates. Organizations are increasingly relying on serverless architectures to focus on application development rather than underlying infrastructure management. By charging based on real consumption, the serverless model minimizes operational complexity, scales automatically, and helps optimise costs. Developers may expect even more flexibility and integration opportunities as serverless technologies grow.
4. AI and Machine Learning Integration:
Cloud computing services are increasingly incorporating artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). Cloud companies are already offering AI/ML-specific services, allowing businesses to design, train, and deploy machine learning models without requiring substantial expertise. This trend enables companies to gain important insights from their data, automate complicated operations, and provide personalized customer experiences. The incorporation of artificial intelligence and machine learning into cloud computing platforms is hastening innovation across industries.

5. Enhanced Security in Cloud Computing:
Organizations shifting to the cloud, continue to prioritize security. In 2023, there will be a greater emphasis on improving cloud security using sophisticated encryption techniques, threat detection, and identity management technologies. To protect sensitive data, maintain compliance, and prevent breaches, cloud providers are investing in rigorous security measures. The cloud security landscape is evolving to secure data integrity and privacy as cyber threats continue to emerge.

Conclusion:
In sum, this landscape is always changing, and 2023 is no exception. The top five trends discussed above – multi-cloud strategies, edge computing integration, serverless computing advancements, AI/ML integration, and enhanced cloud security – are influencing how businesses use cloud services to drive innovation, improve efficiency, and achieve business goals. Staying on top of these trends will be critical for businesses looking to stay competitive and realize the full potential of cloud computing in the coming years.

What Separates Mobile And Cloud Computing From One Another?
Mobile computing is the use of portable devices such as smartphones, tablets, and wearables to access and interact with digital resources and services while on the move. It allows users to communicate, browse, and use applications while on the road. Cloud computing, on the other hand, is the distribution of computer services through the internet, such as storage, processing power, and software.
This paradigm enables users to access and use these resources remotely. This removes the need for extensive local hardware and providing scalable, adaptable, and frequently cost-effective solutions for a variety of applications and sectors. Mobile and cloud computing regularly collide, since mobile devices rely on cloud infrastructure to store data, run programmes, and expand their capabilities.
So, what is the difference between mobile and cloud computing? let’s find out…
Mobile Computation:
1. Device Portability: The concept of this centers around the use of portable devices such as smartphones, tablets, and wearable gadgets. These devices are optimized for mobile use. And programmers design them in such a way that we can use it on the go.
2. Limited Resources: If we compare with traditional computers, mobile devices often have limited processing power, memory, and storage. This limitation exists because of the tiny form factor and the necessity to conserve battery life.
3. Data Storage: The internal storage capacity of mobile devices limits data storage. Locally we can save some data. But that can result in space limits and data loss if the device is destroyed or lost.

4. Local Application Execution: Programmers design applications in mobile computing in a way to execute directly on the device’s hardware. Certain operating systems such as iOS or Android use these apps. They are installed and kept locally on the device. This lets users to interact with them even when they are not connected to the internet.
5. Platform Dependency: Mobile applications are frequently created for a certain platform. E.g. iOS or Android. As a result, developers must design various versions of their apps to support multiple operating systems.
Cloud Computing:
- Remote Application Execution: In cloud computing, programmes are frequently hosted on remote servers. And it is accessible by users via web browsers or dedicated apps. This technique are platform-independent for the programmers. Because users can access apps from a variety of devices and operating systems.
2. Data Storage and Backup: This type of computing provides reliable data storage and backup services. Cloud saves the data on remote servers. This reduces the possibility of data loss due to device damage or loss. Backups are taken on a regular basis to maintain data integrity.

3. Infrastructure Independence: Cloud computing is not dependent on a single device. Instead, external servers and networks provide computing resources, storage, and services. Users can access these resources from a variety of internet-connected devices.
4. Scalable Resources: If we compare with individual machines, cloud services provide essentially endless resources. Programmers can scale up or down these resources to meet various levels of demand. This scalability is especially beneficial for applications with changing consumption patterns.
5. Cross-Platform Compatibility: We can access cloud apps from a variety of devices. E.g. laptops, desktop computers, tablets, and smartphones. This reduces the need for developers to produce separate platforms-specific versions of their programmes.
6. Security and Privacy Concerns: Cloud companies undertake stringent security procedures. But there are still worries regarding data protection and privacy. This is especially true when sensitive data is hosted remotely. Users and organizations must examine cloud providers’ security practises and make informed judgements about data storage.
We’ll learn more about The Top 5 Cloud Computing Craze In This Year later.


