Amazon offers a storage service called Amazon Elastic Block Storage, or Amazon EBS, to be used with your EC2 instances in order to properly address the issues associated with data storage in the cloud. This service offers block level storage volumes with high availability. You will get in-depth information on AWS Amazon EBS Volume in this tutorial on what AWS EBS in Amazon is.
We will learn everything about EBS in this blog post on AWS EBS, which will also cover the following topics in the same order:
- What is AWS EBS in Amazon
- Types of Amazon Elastic Block Store
- Features of AWS EBS
- Benefits of AWS EBS
- Properties of Amazon Elastic Block Store
What is AWS EBS in Amazon?
Let me provide a simple explanation of AWS EBS using an example. Let’s say your computer has 120GB of storage. You purchase an external drive and connect it to your machine since you are running out of space and need more. You’re once more joyful, and life is good. With the exception of the fact that it is intended for use with your EC2 instances (virtual systems) on the AWS cloud, the Amazon EBS is analogous to that external disc.
Let’s now examine AWS EBS Volume in more technical terms.
Although Amazon does provide local storage for each EC2 Instance that you can utilize while the instance is running, the data in that local storage is also destroyed as soon as the instance is shut down. As a result, you would need Amazon EBS with your EC2 instance if you needed to save the data.
Let’s concentrate on a more technical definition of Amazon EBS now that we have a clear understanding of what EBS is in layman’s terms.
The main definition of AWS EBS is that it is a raw block-level storage solution intended for use with Amazon EC2 instances. Every block functions as a hard drive, allowing any kind of file to be stored there or even the installation of an entire operating system. To avoid data loss and component failure, each EBS volume that you attach to your EC2 instance is automatically replicated within its availability zone. With EBS, one can quickly and easily scale their consumption up or down.
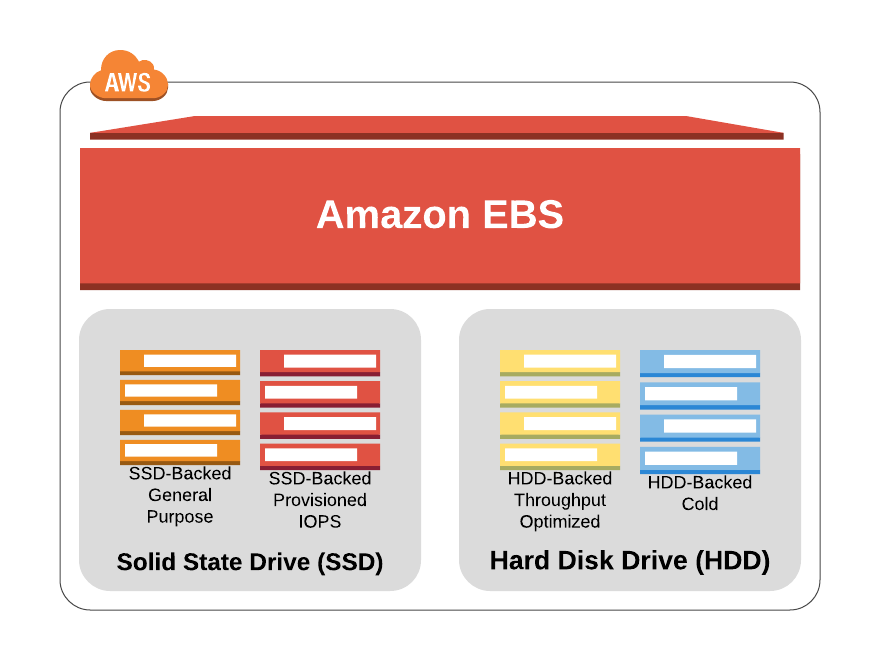
Types of Amazon Elastic Block Store:
For various workloads and use scenarios, AWS offers various EBS volume options. These various EBS volumes are all either SSD (Solid-state drive) or hard disc drive-backed (HDD).
- SSD (Solid-state drive): SSD-backed EBS Volumes are specially tuned for transactional workloads, in which the volume is expected to carry out a large number of tiny read and write operations.
- HDD (Hard Disk Drive): HDD-backed volumes were created with heavy workloads in mind.
The list below includes various EBS Volume types that fit under the SSD-backed and HDD-backed EBS Volume categories.
- Since General Purpose SSD is appropriate for small and medium workloads such regularly accessed workloads, applications in development and production settings, system boot volumes, and more, it is advised for the majority of use cases. 3 IOPS (input/output operations per second) are supported by SSD for each GB. This volume’s size ranges from 1 GiB to 16 TiB.
- Critical production applications and databases that demand high speed EBS storage typically use Provisioned IOPS SSD. The most rigorous I/O workloads can be accommodated by this kind of EBS volume. This volume’s volume size ranges from 4 GiB to 16 TiB.
- Throughput Optimized HDD applications that need a lot of storage and throughput but where IOPS are not important are the ones for which EBS Volumes are intended. such as massive data warehousing, log processing, and other techniques. This volume has a 500 GiB – 16 TiB size.
- Cold HDD is intended for workloads with fewer accesses. This volume is a magnetic storage format that works well in situations where storing data cheaply is typically the major requirement. This volume has a size of 500 GiB – 16 TiB.
Features of AWS EBS :
- Availability and durability: For all of their services, Amazon has made care to guarantee high availability and durability, and EBS is no different in this regard. Amazon replicates the EBS Volume data across many servers in an availability zone at no additional cost in order to prevent data loss. EBS volumes have an annual failure rate (AFR) of 0.1% to 0.2%, which makes them around 20 times more reliable than common commodity disc drives. Traditional disc drives have an annual failure rate of about 4%.

- Amazon EBS Snapshots: According to Amazon Web Services, an EBS Snapshot is an incremental, point-in-time duplicate of an Amazon EBS volume. All the information required to restore your data from EBS volumes is contained in snapshots. When a snapshot is made on an EBS volume for the first time, all of the block data is captured; however, in the subsequent snapshot, just the block modifications since the previous snapshot are captured (provided that the first snapshot still exists while taking the second snapshot). A block’s pictures are all connected together. When data is recovered using an EBS snapshot, both the data unique to that snapshot and the data from earlier snapshots are restored.
- EBS Encryption: For EBS Volumes, AWS also provides seamless data encryption. All data, including data on the volume, disc I/O, and even snapshots made from that encrypted volume, is encrypted when an encrypted EBS volume is mounted to an instance. A secure key management infrastructure does not need to be organized or maintained thanks to this functionality. On the servers that host EC2 instances, EBS encryption takes place. Using Amazon managed keys or keys that customers create themselves using the AWS key management Service, EBS encryption provides data protection (KMS).
Let’s examine the advantages of AWS Elastic Block Store as we continue this tutorial on what is AWS EBS.
Benefits of AWS EBS:
Reliability: EBS Volume may automatically react to its own availability Zone to avoid component failures.
Secure: Who can access which EBS Volumes can be determined using one of the several access control policies that Amazon offers.
Flexibility: EBS Volumes support live configuration changes and can be scaled up and down as needed. without disrupting service, changes to volume type, volume size, and IOPS capacity.
Easy Data Backup: Doing point-in-time snapshots of Amazon EBS volumes that are redundantly stored across different availability zones makes taking data backup simple. Whether or not the EBS Volume is connected to an instance has no bearing on whether or not a snapshot may be taken.
Properties of Amazon Elastic Block Store:
- Only one EC2 instance can have an EBS Volume assigned to it at once.
- The root volume cannot be encrypted without utilizing any of their third-party tools, although volumes other than the root volumes can be encrypted.
- When an EC2 instance is terminated, the root volumes are automatically destroyed.
- An EBS volume can be up to 16 TiB in size.
- To generate volumes in several AWS regions, a copy of the screenshots can be created between the locations.





